Source Code and Binary
Both source code and (independently derived) binary code are provided
within the yaAGC tarball downlod. The files are contained within
a subdirectory named after the software version (such as
"Colossus249" and "Artemis072"). The more important files
supplied are these:
Filename.agc
|
Source code for major
subdivisions of the Colossus
program. |
MAIN.agc
|
Organizer which treats all of
the other assembly-language files (*.agc) as include-files, to form the
complete program.
|
Filename.binsource
|
Human-readable form of the
binary executable as an octal listing.
|
Filename.bin
|
Binary executable created from
binsource (octal listing) file.
|
In other words, to create a
Colossus
binary executable rather than using the one provided with yaAGC
(such as Colossus249.bin), one simply needs to assemble the file
MAIN.agc.
Typically, if all files remain organized the way they are in the yaAGC
distribution tarball, the sequence of steps for doing so (from a
command-line prompt) would be something like this:
cd Colossus249
../yaYUL/yaYUL MAIN.agc
>Colossus249.lst
The binary so produced,
MAIN.agc.bin, should be byte-for-byte identical
to the binary (Colossus249.bin) provided with the yaAGC
distribution. Therefore, the following Linux command should
reveal no differences between the two
diff
MAIN.agc.bin
Colossus249.bin
(Replace "diff" with "fc /b" in Windows.)
Technically speaking....
A point which may not be completely appreciated is that Colossus249.bin
was not created from the
assembly-language source files. Therefore, the
byte-for-byte equivalence mentioned above actually has some
significance. In fact, both the assembly-language source code and
Colossus249.bin (or Colossus249.binsource) come from separate readings
of the original Colossus
assembly listing scan, so their equivalence provides an important check
on validity. (See below.) The file Colossus249.bin was
created from
the human-readable/editable ASCII file Colossus249.binsource by means
of the program Oct2Bin, with
the following steps:
cd Colossus249
../Luminary131/Oct2Bin
<Colossus249.binsource
mv Oct2Bin.bin
Colossus249.bin
Admittedly, few people are likely to perform any processing of this
kind unless contibuting a new version of the Colossus code to the
Virtual AGC project. |
Validation
I generally put a lot of effort into insuring that the executable
binaries being run in the simulated AGC are byte-for-byte (or in the
case of the AGC, word-for-word) identical to the original binaries used
in the spacecraft. Most people won't be interested in this
validation effort at all—just as we're not usually interested in how
food gets from plants and animals onto the plates in front of us as
long as we get our dinners on time; we're happy to trust others to do
the work for us—but for those few of you who wonder if the simulated
AGC really is running the correct code, the following sections provide
explanations. The different program versions are presented in the
order in which they were worked on.
Validity of the Colossus 249 Code
(Apollo 9)
The following description of validation was written prior to having the
Colossus249 software source
code in machine-readable form, and therefore prior to being able to the
core-rope image against the source code as described above. Not
only that, but there were seven errors in the core-rope not detected by
the procedure described below!
So the description is now obsolete. But I like it, and it's my
website, so it stays. (Actually, it continues to have value,
since we don't yet have all versions of the AGC source, and since it
describes how to proceed in the case of recovering poor-quality
assembly listings.)
A Tour of the Source
Materials
Let's look at the
source
materials (actually, a greatly improved version) I've used in
reconstructing
Colossus 1A
(build 249). In
appearance, what we have is a
scan
of a
photocopy of an
assembly listing of the
program. Significant portions of the assembly listing have been
corrupted (or even destroyed) after scanning, seemingly by processing
with the optical-character-recognition capabilities of Adobe
Acrobat. (The
source
materials used for
Luminary
1C, build 131, are generally similar, except that the original
photocopy seems to be of better quality, the scans seem to have been
performed with much more care, and no destructive post-processing has
been performed. On the other hand, the original
Luminary printout seems to have been
on computer paper with green and white color bars, and the remnants of
the green bars make portions of the listing very difficult to read with
certainty. Most of what I have to say will apply to
Luminary as well as to
Colossus.) With some luck,
I'll be able to find (or will be given) better source materials at some
point in the future, but I've had no luck so far in obtaining such
materials and therefore have had to make do with what's available.
An
assembly listing is a type
of report created when a program's source code is processed
("assembled"), in this case by the assembler program called
YUL. (Actually, by
GAP, the successor to
YUL, but when I say "YUL" I really
mean "either YUL or GAP".) Such an assembly listing
contains not only a listing of the source code, but also other helpful
information such as the octal values which the source code assembles
to. The octal codes are what is needed to
run the program, while the source
code is what is needed to
modify
the program. The general layout of the
Colossus (or
Luminary) assembly listing has a
series of sections, of which some of the more interesting are:
- A listing of the source code, side by side with the octal codes
created from the source code, side by side with the addresses at which
the octal values are placed. Click here to
see a typical page (without OCR). The source code is on the
right-hand side of the page, whereas the octal values, addresses, and
other miscellaneous notations are on the left-hand side of the
page. This section occupies about 1500 pages of
the assembly listing.
- A symbol table, giving the addresses at which all of the symbols
created by the program are defined.
- An octal listing, which is the same as the octal values shown
earlier side by side with the source code, but now rearranged so that
the values are arranged by memory address. Click
here to see a typical page (without OCR). This section
occupies about
150 pages of the source listing.
- An octal-to-page cross reference, in which you can find the page
of the assembly listing at which the octal value for any given address
is defined.
Proofing in the Usual Case
From the description above, you will have noted that source code is
listed once within the assembly listing, but that octal values created
from the source code are listed
twice,
and
are therefore redundant. Furthermore, knowing the source
code, one can recreate the octal values from it. (The reverse is
not as easy.) Finally, the octal listing is much shorter than the
source-code listing. Therefore, it shouldn't be surprising that
it is much easier to create a file containing a valid octal listing of
the program than it is to create a file containing a valid source-code
listing.
It is also much easier to
know
that an octal listing is valid than it is to know that a source-code
listing is valid. This is true because the
YUL assembler has added "checksums"
to the octal values, which can be used to verify (or at least give a
high degree of confidence) that the octal values are correct. The
way this works is that the so-called "fixed memory" of the AGC has been
divided into 36 banks, numbered 0-43 in octal notation, each of which
has a 15-bit checksum created by adding up all of the 15-bit words
within the bank. (Actually, the rule for computing the checksum
is more complicated, but that's the basic idea.) Therefore, if we
compute the checksum of a bank and see that it is the same as the
checksum provided by
YUL, we
can be fairly confident that the contents of the bank are
correct. (I should mention that I've provided a utility called
Oct2Bin which is helpful in this
connection. Octal codes can be placed in a simple ASCII file, and
then processed with
Oct2Bin to
create a file containing the actual octal/binary codes and to verify
all bank checksums.)
Another helpful touch added by
YUL
is that each octal value is accompanied by a
parity bit, contrived to make the
number of 1-bits within the octal value (including the parity bit) an
odd number. This is useful in detecting single digit errors of
some kinds. (The digits 0, 3, 5, and 6 have
even parity, while the digits 1, 2,
4, and 7 have
odd parity.
Therefore,
examination of the parity bit could detect substitution of a
'2' for a '3', for example, but not substitution of a '5' for a '6'.)
In almost all cases, the following simple procedure suffices to produce
a valid octal listing:
- Manually proof-read a memory bank of the octal listing against
the original assembly listing, using the redundancy of the octal values
or manually assembling source code as necessary to account for
corrupted areas of the assembly listing.
- Compute and verify the checksum.
- On failure, go back to step 1. On success do the next
memory bank.
Given a valid octal listing, determining the validity of a
source-code
listing is rather trivial: simply run the source code through the
yaYUL assembler, and verify
that the same octal listing is produced.
This procedure in fact suffices for the entire
Luminary octal listing, and for all
memory banks of
Colossus
except banks 35 and 36 (octal). If you want to learn more about
proofing
Colossus memory banks
35 and 36, read onward. Otherwise, quit now!
Postscript: After writing
all of the material below, I was fortunate enough to receive some
much-improved page scans of relevant portions of bank 36 from Mr. Gary
Neff. Therefore, bank 36 is now capable of being proofed by the
simple method explained above. However, it was previously proofed
using the much more complex methods explained below, and therefore I
haven't bothered to change the explanation that follows.
Proofing in
Extraordinary Cases
The simple proofing method outlined above fails when the scan of the
assembly listing for some memory bank is
so corrupted that the bank checksum
or some value(s) within the memory bank are completely unknown.
Sadly, this condition occurs within
Colossus
1C (build 249) banks 35 and 36.
Click here
to see the culprit page of the octal listing. This corrupted page
from the octal listing actually wads together the end of bank 35 and
the beginning of bank 36 in such a way that there is no chance of
figuring out any but a small part of them. In this case, one has
no choice but to use the redundant listing of the octal values that
appears side by side with the source code.
Unfortunately, though, the redundant octal values in the source code
listing fail us here, though in different ways for bank 35 and bank
36. For bank 35, we encounter the problem that the bank checksum
appears
only within the octal
listing and is not redundant. Therefore, we can theoretically
know all of the octal values in the memory bank—if our proofing is
100% accurate—but cannot use the bank checksum to give us the degree
of confidence we would like. For bank 36, the checksum is intact
but some of the octal values cannot be directly determined because of
corruption within the source-code listing. (In other words,
both the octal listing and the
source-code listing are corrupted in the
corresponding place.) As far
as proofing is concerned, however, the conclusion is the same: We
need some method of proofing which gives us a high level of confidence
in the result, in the absence of a checksum.
Here is the alternate method of proofing used in this cases, which
seems to offer a fairly high level of confidence:
- Note first that each memory bank actually occupies 4 pages within
the octal listing. For this method, we proof each memory page
separately from the others.
- Manually proof-read the memory page, using either the octal
listing or the source-code listing as desired or appropriate.
While doing so, record the number of digits which have been corrected.
- Repeat step 2 until zero corrections have been made in two
successive proofings.
- To the extent feasible, one of the 0-error proofings should use
the octal listing, and the other should use the source-code listing.
The theory behind this procedure is that in any given proofing a
certain percentage of errors is corrected, and that by monitoring the
number of errors that have been corrected we can get a good sense of
the number of errors remaining. To take a "typical" case, suppose
that on the first proofing 100 errors are detected and corrected, on
the second proofing 1 error is detected and corrected, and on the third
and fourth proofings 0 errors are detected. It would be
reasonable to suppose that each proofing pass detects 99% of errors, so
the expected number of errors remaining after the 4th pass is
100*0.01*0.01*0.01*0.01, or about a millionth of an error. Of
course, this reasoning assumes that our ability to detect and correct
different errors has some quality of statistical independence, and that
errors are not remaining undetected through some systematic
problem. We try to overcome that objection by making sure that we
use both the octal listing and the source-code listing in the proofing
process, but how successful we have been is always debatable.
As far as proofing is concerned, this technique suffices for
Colossus banks 35 and 36, but does
not actually give us a 100% knowledge of the octal values within the
banks. For bank 35, we can simply construct a checksum and be
done with it. But for bank 36, we need to do a little more
work. If you want to know more about that, read onward!
When All
Else Fails—Digital Archaeology
In a case like bank 36, the technique above may give us confidence that
all octal values that are legible in the page images are keyed
accurately, but the proofing technique can't give us
any insight into the octal values that are simply missing from both the
source-code listing and the octal listing. One trick we can try
is to compare the
Colossus
and
Luminary source-code,
which actually have a high degree of overlap in general.
Unfortunately, this
is not a case in which there is any such overlap, so the comparison is
of no help.
Click
here (p. 846) and
here
(p. 847) to
see the pages of the source-code listing that are relevant to the
problems in bank 36, namely:
- Address 36,2634: This source-code line is simply
missing. We have no clue as to what may have been in it, except
that it is seemingly the first
part of a double-precision constant
whose second part is the word
00000 octal.
- Address 36,2734: Appears to be interpretive code reading "something1 something2", but only a
couple of pixel rows are present, and so neither the octal code nor the
assembly-language code can be read.
- Address 36,2742: Highly corrupted, but may have the octal code 00021 and may have interpretive source code
reading "16D".
- Address 36,2747: Pretty corrupted, but seems likely to be
the interpretive source code "CALL" with octal code 77624.
As far as points 3 and 4 are concerned, I think it's pretty easy to
convince ourselves that the proposed interpretations are probably
correct. If you want a challenge, you may like to try solving
problems 1 and 2 for yourself, before continuing to read my proposed
solution below.
Point 2 is somewhat trickier than problems 3 and 4, because the
corruption of the page-image is so much
greater. But with some effort, we can still figure it out.
Within the
offending page of the source-code
listing, notice the notations "REF" and "LAST". These notations
appear only on source-code lines referencing variables. "REF"
gives the number of times the variable has been referred to so far in
the assembly listing, which "LAST" gives the page number on which the
preceeding reference occurred. The problematic source line
clearly contains REF and LAST notations (even though we cannot read
them), and so it is clear that
something2
is the name of a variable. You should be able to convince
yourself fairly easily that the variable in question is
RCON. In
other words,
something2="
RCON". (In case it's
still not obvious
how you
would convince yourself of this, note that "REF 6" to
RCON is below the missing
source line, while "REF 4" is on the preceding page, but that "REF 5"
is nowhere to be found.) Next, because this
section of code is AGC interpreter language (rather than assembly
language), we can narrow down the choices for
something1; theoretically, the only
possibilities are
STORE,
STODL, or
STOVL. Simply in terms of
appearances, it seems likely that
something1=
STODL. Unfortunately, the
interpreter documentation (
Users Guide to the Block II AGC/LGC
Interpreter, by Charles A. Muntz) was last updated in early
1965, and contains an incorrect numerical opcode for
STODL. Not to be
deterred, though, if we look at the other source-code lines near the
missing line, we see intact lines like "
STODL RPRE," (the comma after "
RPRE", by the way, is actually
part of the variable name), from which we can deduce that the octal
code for
STODL is
16000. Noting that
RCON
has the address 1635, therefore, "
STODL
RCON" must assemble to the octal code 16000+1635+1=17636.
But—and why, I'd like to know, does there always seem to be
another "but"?—the missing line
of code is preceded by a line of source code reading simply "
STADR". The
STADR opcode has the odd effect
of complementing the code that follows it.
Therefore—finally!—the missing octal code for address 36,2734 is
probably 60141. This closely matches the remaining pixel
fragments (and
expected parity bit) of the missing line, and so we can feel good about
it.
Having now determined all of the octal values within the bank except at
address 36,2634, and noting the checksum for bank 36 is known, we can
consider the possibility of recreating the octal value at 36,2634
simply by putting a value there that correctly reproduces the bank's
checksum. This is actually trickier than you may suppose, since
the checksum is unique only up to a sign. (In other words, we
don't know whether to insert a value that produces the positive
checksum or one that produces the negative checksum.) Often,
either the positive or the negative checksum will be impossible to
produce, thus removing the uncertainty. Where it is possible to
produce both the positive and the negative checksum, we note that 90%
of the memory banks have positive checksums, so we have a much better
chance of being correct if we choose the positive checksum.
All of this turns out to be an anti-climax, however: Prior to
any of the reasoning listed above, our inclination was simply to put
00000 at address 36,2634. Remarkably, this produces the correct
bank checksum without any additional work on our part! Perhaps
this is the first time in history that a
gut reaction has been confirmed by checksum.
Happy Epilogue!
After the all of the intricate reasoning above was worked out—and the
description above written—Mr. Gary Neff was able to send me some
terrific replacement scans of the problematic assembly-listing pages
from bank 36, namely pp. 846-847. If
you examine locations
36,2634, 36, 2734, 36,2742, and 36,2747 on the new scan, you'll see
that they indeed contain exactly the values deduced above! I
still think the exploration I went through before receiving the new
scans is a valuable illustration of technique, not to mention being
soothing to my ego, so I'll leave it in place for future generations to
enjoy. :-)
Validity of the Comanche 055 Code
(Apollo 11)
The Comanche 055 page images became available after the Colossus 249
and Luminary 131page images had already been converted to source-code
files, and prior to any other missions becoming available. The
conversion technique was very abbreviated compared to that of Colossus
249, as follows:
- A small corps of volunteers—thanks (in alphabetical order)
Fabrizio Bernardini, Hartmuth Gutshe, Onno Hommes, Jim Lawton, and
Sergio Navarro!—took
the existing Colossus 249 source-code files, or on occasion the
Luminary 131 source-code files, and laboriously compared
them line-by-line to the Comanche 055 assembly-listing page images,
porting the differences they found.
- The resulting Comanche 055 source code was assembled using yaYUL
to produce a binary executable, which was horribly wrong at this point
(with dozens of conversion errors),
but was used to create a "binsource" file (which is an octal listing of
the entire program).
- The binsource file was laboriously proofed against the octal
listing in the page images (this time by me), and corrected. As a
double-check, the bank checksums are all correct.
- Finally, at every point where the binary created from the source
code by yaYUL
differed from the binsource file, the source code was compared to the
page images and corrected. After all corrections were made, the
binary
created by yaYUL was identical
to the binary created from the binsource file.
The binary thus produced by
yaYUL
is supplied in the source tree and used for regression testing.
Validity of Artemis 072 Code
(Apollo 15-17)
The Artemis 072 executable (Artemis072.bin) was created by manually
entering binary data from scans of an Artemis 072 assembly
listing. The
data was proofed and reproofed until the bank checksums, as described
above, were correct, and the binary was made available to the public on
2006-01-10. On 2010-02-20 (more than 4 years later), source code
was finally available and assembled.
A single error which did not
affect the memory-bank checksum was found and corrected in
the binary. So we are
now
confident that what is being provided is both complete and correct.
This is an interesting object lesson. My previous notes in this
section, prior to the availability of source code, made it clear that I
wouldn't be surprised if additional pairs or even triplets of errors
were found in the binary ... but the notion that an unpaired error
might still exist which did not affect the checksum never occurred to
me. The problem is a weakness in the checksumming algorithm used
in the AGC.
If the AGC had used a "normal" checksumming algorithm (from the modern
point of view) with 2's-complement arithmetic, any
single error in data would have
caused the checksum to change, and the error to be detected.
But in the 1's-complement arithmetic of the AGC, simple checksumming
does not have the same desirable property. For example, since
there is both a +0 and a -0, which produce the same result in an
addition, a memory error in which +0 is replaced by -0 (or vice versa)
produces the same checksum and would be undetectable. But
algorithmically the problem is more complicated than that, since a
simple checksum algorithm was not used. The actual algorithm used
on a data-word by data-word basis was this:
- The next data word is added to the running checksum.
- If there is positive
overflow, the result is reduced by 040000 (considered as a positive
number, thus preserving the sign of the result) and then incremented.
- if there is negative
overflow, the result is incremented by 040000 (again, considered as a
positive number, thus preserving the sign of the result), and then
decremented.
For example, if the running checksum was 030000 (a positive number),
and the next data word
was 020000 (another positive number), then adding them would give
050000 (arithmetic overflow!),
which would be decremented (due to the overflow) by 040000 to give
010000, and then incremented by 1 to give a running checksum of 010001.
If you are amused by such stuff, I invite you to consider the ways in
which such an algorithm might fail to detect error. In the case
of the Artemis 72 binary, the now-corrected error was a
single bit (the most significant
bit) of a single memory location.
Validity of Colossus 237 (Apollo 8)
At this writing (2009-08-09), we have page images of the Colossus 237
program listing, but haven't yet created buildable source-code files or
an executable binary from the page images. So my comment below
are really musings about what will need to be done eventually rather
than a report of work that has actually been done.
The Colossus 237 program listing presents a special challenge, because
the only physical copy we've had access to is truncated. It
contains all of the source code, as well as the binary words associated
with the source code on a line-by-line basis. But it is missing
the octal listing that condenses all of the binaries into an easily
accessible form. Because the octal listing is missing, the
"bugger words" that are used to make the memory-bank checksums compute
correctly are also missing. Thus, important redundancies and
checksums that normally would be used to provide confidence of
correctness are missing.
Therefore, the following unique validation procedure was applied
instead:
- A "binsource" file was created by laboriously stepping through
the page images of the program listing, line-by-line, and observing the
listed binary words. The "bugger words" are not available in this
fashion, and are therefore left at zero.
- Since Colossus 237 and Colossus 249 are separated in time by only
a few months, the binsource file of Colossus 237 and Colossus 249 were
compared using automated tools ('diff' or similar). Where
differences existed, the page images of the Colossus 237 program
listing were referenced to verify (to the extent possible) that the
differences were real rather than being transcription errors.
- Where complete memory banks were found to be identical by the
automated comparison, the bugger words were copied from Colossus 249 to
Colossus 237.
- Source-code files were created from the page images of the
program listing.
- The binary of the assembled source-code files was compared in an
automated fashion against the binary created from the binsource file,
and either the binsource file or the source code (or both) were
corrected when any discrepancies were found.
- For any banks remaining without bugger words in the binsource
file, the bugger words created by yaYUL
were added.
Validity of
Solarium 055 (Apollo 4)
Solarium 055 presents a big challenge because it is the first Block I
code processed, and no Block I support was previously provided by the
yaYUL assembler.
... TBD ...


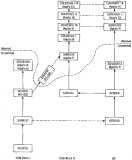 Programs
with names like Sundisk, Solarium, and Sunspot were pre-Colossus versions of
the Command Module
AGC's software. They were not forms of Colossus as such, but provided some
code for Colossus.
If you click on the image to the right, you can see a family tree (or
at least the earlier portions of a family tree) for Colossus.
Programs
with names like Sundisk, Solarium, and Sunspot were pre-Colossus versions of
the Command Module
AGC's software. They were not forms of Colossus as such, but provided some
code for Colossus.
If you click on the image to the right, you can see a family tree (or
at least the earlier portions of a family tree) for Colossus.